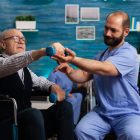
Falls are a common problem in the elderly population, and they can lead to significant health consequences, such as fractures, head injuries, and loss of independence. Physiotherapy plays a vital role in preventing falls and improving balance in the elderly population. Here are some of the ways in which physiotherapy can help:
Balance exercises: Physiotherapists can design specific exercises to improve balance in the elderly population. These exercises may include standing on one leg, walking heel to toe, and other exercises that challenge balance.
Strength training: Physiotherapists can design exercises to improve strength in the lower body, which can help prevent falls. These exercises may include squats, lunges, and leg presses.
Flexibility exercises: Physiotherapists can design exercises to improve flexibility, which can help prevent falls. These exercises may include stretching and range-of-motion exercises.
Education: Physiotherapists can educate elderly patients on ways to prevent falls, such as clearing clutter from the home, wearing proper footwear, and using assistive devices like canes or walkers.
Environmental modifications: Physiotherapists can assess the home environment and recommend modifications to make it safer and more accessible, such as installing grab bars in the bathroom or improving lighting in the home.
Overall, physiotherapy plays a crucial role in preventing falls and improving balance in the elderly population. By designing specific exercise programs, educating patients on fall prevention strategies, and making environmental modifications, physiotherapists can help seniors maintain their independence and avoid the negative health consequences of falls.
Balance training –
It is an important component of exercise for the elderly population because it can help prevent falls and improve overall mobility and quality of life. Here are some key considerations and exercises to keep in mind when designing a balance training program for the elderly:
Safety first: When working with elderly clients, safety should always be the top priority. Ensure that the exercise area is free of hazards, and use equipment such as balance pads or stability balls that are appropriate for the individual’s skill level.
Start slow and progress gradually: Begin with simple balance exercises, such as standing on one leg or walking heel to toe, and gradually increase the difficulty level as the individual’s balance improves.
Incorporate a variety of exercises: It’s important to work on different aspects of balance, including static balance (maintaining balance while standing still), dynamic balance (maintaining balance while moving), and reactive balance (responding to sudden changes in direction or surface). Exercises can include standing on an unstable surface, such as a balance board or wobble cushion, or practicing yoga poses that challenge balance, such as tree pose or warrior III.
Include strength training: Building strength in the lower body can also improve balance. Exercises such as squats, lunges, and calf raises can be incorporated into a balance training program.
Consider individual needs and abilities: When designing a balance training program for the elderly, it’s important to take into account any health conditions or physical limitations the individual may have. A physical therapist or qualified fitness professional can help tailor the program to meet the individual’s specific needs and abilities.
Overall, balance training is an important component of exercise for the elderly population, and can help improve mobility, prevent falls, and enhance overall quality of life
Strength training –
It is an essential component of any fitness routine, regardless of age. In fact, strength building in the elderly population is particularly important, as it can help prevent the loss of muscle mass and function that often occurs with aging. Here are some tips for building strength in the elderly population:
Consult with a healthcare provider: Before beginning any strength-building program, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure that it is safe and appropriate for your individual needs.
Start slowly: It is important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your strength-building program. This can help prevent injury and ensure that your muscles and joints have time to adapt to the new demands.
Focus on compound exercises: Compound exercises, such as squats, lunges, and push-ups, engage multiple muscle groups at once and can help improve overall strength and function.
Use resistance bands or light weights: Resistance bands or light weights can be a great way to add resistance to your exercises without putting too much strain on your joints. They can also help improve balance and coordination.
Incorporate balance exercises: Balance exercises, such as standing on one leg or walking heel to toe, can help improve balance and reduce the risk of falls.
Rest and recover: It is important to give your muscles time to rest and recover between strength-training sessions. This can help prevent injury and ensure that your muscles have time to rebuild and grow.
Overall, strength building is an important component of any fitness routine, regardless of age. By starting slowly, focusing on compound exercises, incorporating resistance bands or light weights, and incorporating balance exercises, elderly individuals can improve their strength, function, and overall quality of life