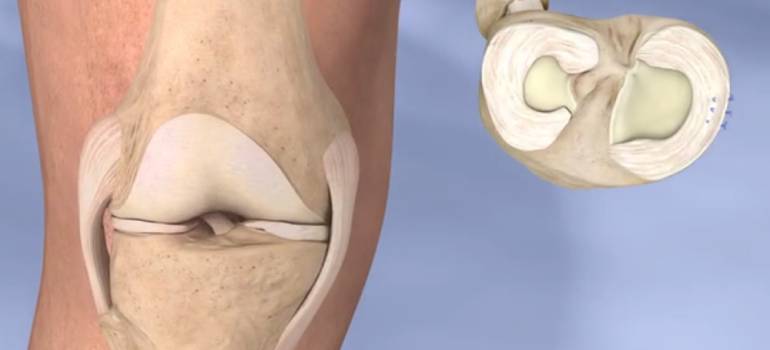
Anatomy of meniscus
Meniscus is a C or horseshoe-shaped fibrocartilaginous structure that sits between the femur and tibial condyles. The medial meniscus is present on the medial tibial condyle and attached to the medial collateral ligament while the lateral meniscus is present on the lateral condyle of the tibia but does not attach to the corresponding lateral collateral ligament. Due to this, the lateral meniscus is less prone to injuries than the medial meniscus. Each meniscus is thinner at the middle of the joint and gets thicker as it gets nearer to the joint lining.
The major functions of menisci are:
- Provide greater stability to the knee joint
- Works as the shock absorber of the joint.
- Evenly distribute the weight and prevent the rubbing of bones.
- It also protects the adjacent tendons and improves its mechanical effect.
Meniscal Tear
Meniscus tear is one the most common injuries of knee joint. Athletes, especially those who participate in contact sports, are at higher risk of suffering a meniscus tear. However, people of any age can tear off the meniscus either due to degeneration or sudden injury to the knee. You may also feel a “pop” when you tear the meniscus apart. Many people can still walk on injured knees, and many athletes can continue to play. However, within two to three days, the knee will slowly become swollen and stiff. Other than this, symptoms like knee pain, swelling, locking of knee joint, feeling of ‘giving away’, and restricted knee range of motion can also be seen in meniscal injury.
Treatment of Meniscal Tear
Treatment is mainly based on the severity, size, and location of tear. In the case of grade 1 and grade 2 tear, if symptoms are mild and no signs of locking or restriction of the joint range are present then conservative treatment is recommended by the doctor.
Conservative Treatment
-
- PRICE protocol: Protection, rest, ice, compression and elevation are effective in reducing pain and swelling.
- NSAID’s: Ibuprofen and aspirin are helpful in relieving symptoms like pain and swelling.
- Corticosteroid injections
- Regenerative procedure: Platelet-rich plasma injections are the advance techniques which are presently being studied to find out the effectiveness in meniscal repair.
- Physical therapy: As part of your recovery, you may begin physical therapy. First, you will exercise to improve the range of motion of your knees. When your knee is healed, you will begin strengthening exercises. You will learn how to practice in your physical therapy appointment. Then you will do it yourself at home. These exercises are one of the most critical parts of the recovery process. Therefore, stick to the plan and carefully follow all the therapist’s instructions.
Strengthening exercises: Quadriceps and hamstring exercises improve the muscle strength and improve the overall function of the knee. Following exercises can be done to improve the muscle strength:
- Mini Squats: It helps in strengthening the quadriceps, the large muscles in the front of the thighs, without putting too much pressure on the knees.
- Quadriceps setting
- Straight leg raises
- Hamstring curls
- Clam shell
- Standing heel raises
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment fails or the tear is severe i.e., grade 3 then it might need surgical treatment to repair. The following surgeries are usually recommended by the doctor:
- Arthroscopic repair: In this procedure, your doctor will make slight cut in your knee joint. Then they will insert an arthroscope inside your joint to look for the tear. Once they find the tear, they will place small devices like dart at tear to sew it up. The stitches will gradually get dissolve in the body.
- Arthroscopic parital menisectomy: During this procedure, doctor will remove the torn part meniscus, so that normal knee range of motion can be regain.
- Arthroscopic total menisectomy: This procedure is mainly done when the major part of meniscus is damaged. In this, whole meniscus is removed.
Post surgery recovery
To keep your knee stable you may need to wear a brace or cast. You may also have to use crutches for at least a month to reduce the burden on your knees. Your doctor may recommend physical therapy as part of your recovery. It can help you increase your range of motion and help your knees become stronger. They may also share some exercises you can do at home. If you have had a partial or full meniscectomy, your recovery time will be approximately one month. If your meniscus is repaired, it may take up to 3 months.